Mybatis练习
Mybatis练习
目标
- 能够使用映射配置文件实现CRUD操作
- 能够使用注解实现CRUD操作
1. 配置文件实现CRUD
一般项目里面包含了品牌数据的 查询 、按条件查询、添加、删除、批量删除、修改 等功能,而这些功能其实就是对数据库表中的数据进行CRUD操作。接下来我们就使用Mybatis完成品牌数据的增删改查操作。以下是我们要完成功能列表:
- 查询
- 查询所有数据
- 查询详情
- 条件查询
- 添加
- 修改
- 修改全部字段
- 修改动态字段
- 删除
- 删除一个
- 批量删除
我们先将必要的环境准备一下。
1.1 环境准备
-
数据库表(tb_brand)及数据准备
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23-- 删除tb_brand表
drop table if exists tb_brand;
-- 创建tb_brand表
create table tb_brand
(
-- id 主键
id int primary key auto_increment,
-- 品牌名称
brand_name varchar(20),
-- 企业名称
company_name varchar(20),
-- 排序字段
ordered int,
-- 描述信息
description varchar(100),
-- 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
status int
);
-- 添加数据
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values ('三只松鼠', '三只松鼠股份有限公司', 5, '好吃不上火', 0),
('华为', '华为技术有限公司', 100, '华为致力于把数字世界带入每个人、每个家庭、每个组织,构建万物互联的智能世界', 1),
('小米', '小米科技有限公司', 50, 'are you ok', 1); -
实体类 Brand
在
com.itheima.pojo包下创建 Brand 实体类。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16public class Brand {
// id 主键
private Integer id;
// 品牌名称
private String brandName;
// 企业名称
private String companyName;
// 排序字段
private Integer ordered;
// 描述信息
private String description;
// 状态:0:禁用 1:启用
private Integer status;
//省略 setter and getter... 自己写时要补全这部分代码
} -
编写测试用例
测试代码需要在
test/java目录下创建包及测试用例。项目结构如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13mybatis-demo
├── src
│ ├── main
│ │ ├── java
│ │ └── resources
│ └── test
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── itheima
│ │ └── test
│ │ └── MyBatisTest.java
│ └── resources
└── pom.xml -
安装 MyBatisX 插件
-
MybatisX 是一款基于 IDEA 的快速开发插件,为效率而生。
-
主要功能
- XML映射配置文件 和 接口方法 间相互跳转
- 根据接口方法生成 statement ,即根据接口自动生成配置文件中的SQL语句
-
安装方式
点击
file,选择settings,点击Plugins,搜索MybatisX安装,MybatisX 图标如下,是一只小鸟
注意:安装完毕后需要重启IDEA
-
插件效果
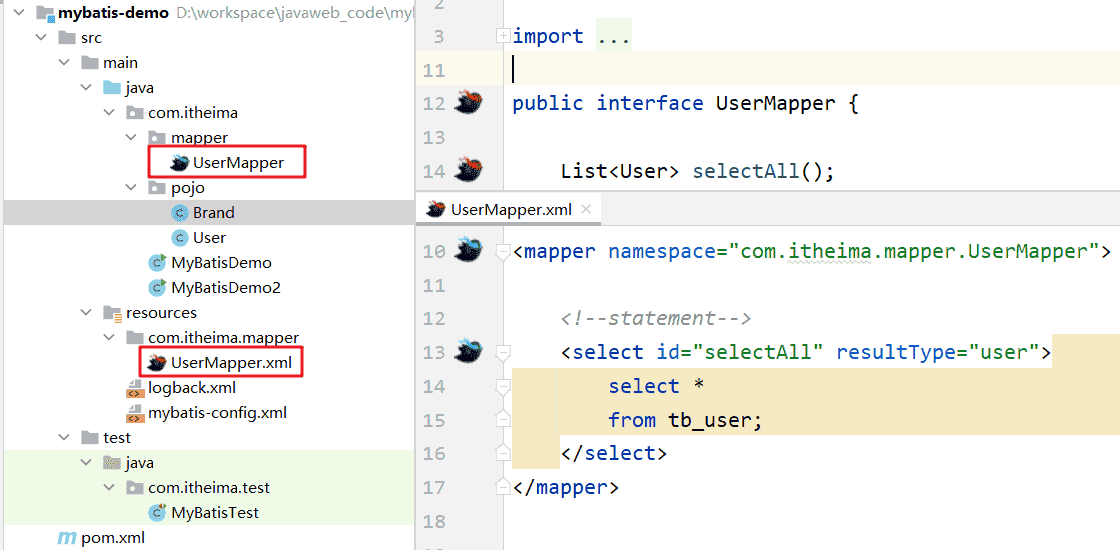
红色头绳的表示映射配置文件,蓝色头绳的表示mapper接口。在mapper接口点击红色头绳的小鸟图标会自动跳转到对应的映射配置文件,在映射配置文件中点击蓝色头绳的小鸟图标会自动跳转到对应的mapper接口。也可以在mapper接口中定义方法,**在爆红的地方使用
alt + 回车,自动生成statement,自动生成映射配置文件中的statement**,如图所示
-
1.2 查询所有数据
接下来我们就来讲查询所有数据功能,而实现该功能我们分以下步骤进行实现:
-
编写接口方法:Mapper接口
-
参数:无
查询所有数据功能是不需要根据任何条件进行查询的,所以此方法不需要参数。
1
List<Brand> selectAll();
-
结果:List
我们会将查询出来的每一条数据封装成一个
Brand对象,而多条数据封装多个Brand对象,需要将这些对象封装到List集合中返回。 -
执行方法、测试
-
1.2.1 编写接口方法
在 com.itheima.mapper 包写创建名为 BrandMapper 的接口。并在该接口中定义 List<Brand> selectAll() 方法。
1 | public interface BrandMapper { |
1.2.2 编写SQL语句
在 reources 下创建 com/itheima/mapper 目录结构,并在该目录下创建名为 BrandMapper.xml 的映射配置文件
1 |
|
1.2.3 编写测试方法
在 MybatisTest 类中编写测试查询所有的方法
1 |
|
注意:现在我们感觉测试这部分代码写起来特别麻烦,我们可以先忍忍。以后我们只会写上面的第3步的代码,其他的都不需要我们来完成。
执行测试方法结果如下,以下为日志输出: (其中注释是自己补的)
1 | [DEBUG] 12:19:32.403 [main] c.i.m.B.selectA11 - ==> Preparing: select * from tb_brand; // 执行的sql语句 |
从上面结果我们看到了问题,有些数据封装成功了,而有些数据并没有封装成功。像id、ordered等封装成功,brandName和companyName就封装失败,为什么这样呢?
实体类属性名 和 数据库表列名 不一致,不能自动封装数据
- **起别名:**在SQL语句中,对不一样的列名起别名,别名和实体类属性名一样
- 可以定义
片段,提升复用性 - **resultMap:**定义
完成不一致的属性名和列名的映射
这个问题可以通过两种方式进行解决(第二个方法更常用):
- 给字段起别名
- 使用resultMap定义字段和属性的映射关系
1.2.4 起别名解决上述问题
从上面结果可以看到 brandName 和 companyName 这两个属性的数据没有封装成功,查询 实体类 和 表中的字段 发现,在实体类中属性名是 brandName 和 companyName ,而表中的字段名为 brand_name 和 company_name。那么我们只需要保持这两部分的名称一致这个问题就迎刃而解。
我们可以在写sql语句时给这两个字段起别名,将别名定义成和属性名一致即可。
1 | <select id="selectAll" resultType="brand"> |
而上面的SQL语句中的字段列表书写麻烦,如果表中还有更多的字段,同时其他的功能也需要查询这些字段时就显得我们的代码不够精炼。Mybatis提供了sql 片段可以提高sql的复用性。
SQL片段:
-
将需要复用的SQL片段抽取到
sql标签中1
2
3<sql id="brand_column">
id, brand_name as brandName, company_name as companyName, ordered, description, status
</sql>id属性值是唯一标识,引用时也是通过该值进行引用。
-
在原sql语句中进行引用
使用
include标签引用上述的 SQL 片段,而refid指定上述 SQL 片段的id值。1
2
3
4
5<select id="selectAll" resultType="brand">
select
<include refid="brand_column" />
from tb_brand;
</select>
1.2.5 (推荐) 使用resultMap解决上述问题
起别名 + sql片段的方式可以解决上述问题,但是它也存在问题。如果还有功能只需要查询部分字段,而不是查询所有字段,那么我们就需要再定义一个 SQL 片段,这就显得不是那么灵活。
那么我们也可以使用resultMap来定义字段和属性的映射关系的方式解决上述问题。
-
在映射配置文件中使用resultMap定义 字段 和 属性 的映射关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13// id:唯一标识 type:映射的类型,支持别名,映射结果的 Java 类型,这里是 brand 类型。
<resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand">
<!--
id:完成主键字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
result:完成一般字段的映射
column:表的列名
property:实体类的属性名
-->
<result column="brand_name" property="brandName"/>
<result column="company_name" property="companyName"/>
</resultMap>注意:在上面只需要定义 字段名 和 属性名 不一样的映射,而一样的则不需要专门定义出来。
-
SQL语句正常编写
1
2
3
4<select id="selectAll" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand;
</select>
1.2.6 小结
实体类属性名 和 数据库表列名 不一致,不能自动封装数据
- **起别名:**在SQL语句中,对不一样的列名起别名,别名和实体类属性名一样
- 可以定义
片段,提升复用性
- 可以定义
- **resultMap:**定义
完成不一致的属性名和列名的映射
而我们最终选择使用 resultMap的方式。查询映射配置文件中查询所有的 statement 书写如下:
1 | <resultMap id="brandResultMap" type="brand"> |
1.3 查询详情
有些数据的属性比较多,在页面表格中无法全部实现,而只会显示部分,而其他属性数据的查询可以通过 查看详情 来进行查询。
查看详情功能实现步骤:
-
编写接口方法:Mapper接口
1
Brand selectById(int id);
-
参数:id
查看详情就是查询某一行数据,所以需要根据id进行查询。而id以后是由页面传递过来。
-
结果:Brand
根据id查询出来的数据只要一条,而将一条数据封装成一个Brand对象即可
-
-
编写SQL语句:SQL映射文件,以下代码中的parameterType可以省略
1
2
3<select id="selectByld" parameterType="int" resultType="brand">
select "from tb_brand where id =#{id};
</select> -
执行方法、进行测试
1.3.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义根据id查询数据的方法
1 | /** |
1.3.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写 statement,使用 resultMap 而不是使用 resultType
1 | <select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
注意:上述SQL中的参数 #{id}先这样写,一会我们再详细讲解
1.3.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
执行测试方法结果的部分日志信息如下:
1 | [BUG] 15:51:35.400 [main] c.i.m.B.selectById -==> Preparing: select * from tb_brand where id = ?; //SQL语句 |
1.3.4 参数占位符
查询到的结果很好理解就是id为1的这行数据。而这里我们需要看控制台显示的SQL语句,能看到使用?进行占位。说明我们在映射配置文件中的写的 #{id} 最终会被 ?进行占位。接下来我们就聊聊映射配置文件中的参数占位符。
mybatis提供了两种参数占位符,主要使用第一个#{}:
-
#{} :执行SQL时,会将 #{} 占位符替换为?,将来自动设置参数值。从上述例子可以看出使用#{} 底层使用的是
PreparedStatement -
${} :拼接SQL。底层使用的是
Statement,会存在SQL注入问题。如下图将 映射配置文件中的 #{} 替换成 ${} 来看效果1
2
3
4<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand where id = ${id};
</select>重新运行查看结果如下:
1
2
3[BUG] 15:51:35.400 [main] c.i.m.B.selectById -==> Preparing: select * from tb_brand where id = 1; //直接将数据拼接到SQL语句中
[BUG] 15:51:35.437 [main] c.i.m.B.selectById -==> Parameters: 1(Integer) // 传递的参数值
[BUG] 15:51:35.460 [main] c.i.m.B.selectById - ==> Brand{id=1, brandName='三只松鼠',companyName='三只松鼠股份有限公司',ordered=5, description='好吃不上火',status=0} // 查询到的结构
注意:从上面两个例子可以看出,以后开发我们使用 #{} 参数占位符
1.3.5 parameterType使用
对于有参数的mapper接口方法,我们在映射配置文件中应该配置 ParameterType 来指定参数类型。只不过该属性都可以省略。如下图:
1 | <select id="selectById" parameterType="int" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
1.3.6 SQL语句中特殊字段处理
以后肯定会在SQL语句中写一下特殊字符,比如某一个字段大于某个值,如下图
1 | <select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
在IDEA中可以看出报错了,因为映射配置文件是xml类型的问题,而 > < 等这些字符在xml中有特殊含义,所以此时我们需要将这些符号进行转义,可以使用以下两种方式进行转义
-
转义字符
下图的
<就是<的转义字符。1
2
3
4
5<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where id < #{id}
</select> -
,直接输入大写的`CD`会有自动提示
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9<select id="selectById" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where id
<![CDATA[
<
]]>
#{id}
</select>
1.4 多条件查询
我们经常会遇到多条件查询,像是同时通过企业名称和品牌名称来查询,而我们做这个功能需要分析最终的SQL语句应该是什么样,思考两个问题
- 条件表达式
- 如何连接
条件字段 企业名称 和 品牌名称 需要进行模糊查询,所以条件应该是:
1 | select * from tb_brand where status = ? and company_name like ? and brand_name like ?; |
简单的分析后,我们来看功能实现的步骤:
-
-
编写接口方法
-
参数:所有查询条件
-
结果:List
-
-
-
- 在映射配置文件中编写SQL语句
-
- 编写测试方法并执行
1.4.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义多条件查询的方法。
而该功能有三个参数,我们就需要考虑定义接口时,参数应该如何定义。Mybatis针对多参数有多种实现
-
使用
@Param("参数名称")标记每一个参数,在映射配置文件中就需要使用#{参数名称}进行占位1
List<Brand> selectByCondition( int status, String companyName, String brandName);
-
将多个参数封装成一个 实体对象 ,将该实体对象作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和实体类属性名保持一致。1
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Brand brand);
-
将多个参数封装到map集合中,将map集合作为接口的方法参数。该方式要求在映射配置文件的SQL中使用
#{内容}时,里面的内容必须和map集合中键的名称一致。1
List<Brand> selectByCondition(Map map);
1.4.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写 statement,使用 resultMap 而不是使用 resultType
1 | <select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
1.4.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
1.4.4 动态SQL
上述功能实现存在很大的问题。用户在输入条件时,肯定不会所有的条件都填写,这个时候我们的SQL语句就不能那样写的
例如用户只输入 当前状态 时,SQL语句就是
1 | select * from tb_brand where status = #{status} |
而用户如果只输入企业名称时,SQL语句就是
1 | select * from tb_brand where company_name like #{companName} |
而用户如果输入了 当前状态 和 企业名称 时,SQL语句又不一样
1 | select * from tb_brand where status = #{status} and company_name like #{companName} |
针对上述的需要,Mybatis对动态SQL有很强大的支撑,可以使用if等语句决定哪些部分需要和不需要:
if
choose (when, otherwise)
trim (where, set)
foreach
我们先学习 if 标签和 where 标签:
-
if 标签:条件判断
- test 属性:逻辑表达式
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
where
<if test="status != null">
status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</select>如上的这种SQL语句就会根据传递的参数值进行动态的拼接。如果此时status和companyName有值那么就会值拼接这两个条件。
执行结果如下:
1
2
3
4
5//日志输出
selectByCondition -==> Preparing: select from tb_brand where status = ? and company_name like ?
selectBycondition -==> Parameters: 1 (Integer), %华为%(String)
selectByCondition -==> Total: 1但是它也存在问题,如果此时给的参数值是
1
2
3
4Map map = new HashMap();
// map.put("status" , status);
map.put("companyName", companyName);
map.put("brandName" , brandName);拼接的SQL语句就变成了
1
select * from tb_brand where and company_name like ? and brand_name like ?
而上面的语句中 where 关键后直接跟 and 关键字,这就是一条错误的SQL语句。这个就可以使用 where 标签解决
-
where 标签
- 作用:
- 替换where关键字
- 会动态的去掉第一个条件前的 and
- 如果所有的参数没有值则不加where关键字
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<select id="selectByCondition" resultMap="brandResultMap">
select *
from tb_brand
<where>
<if test="status != null">
and status = #{status}
</if>
<if test="companyName != null and companyName != '' ">
and company_name like #{companyName}
</if>
<if test="brandName != null and brandName != '' ">
and brand_name like #{brandName}
</if>
</where>
</select>注意:需要给每个条件前都加上 and 关键字。
- 作用:
1.5 单个条件(动态SQL)
若在查询时只能选择 品牌名称、当前状态、企业名称 这三个条件中的一个,但是用户到底选择哪儿一个,我们并不能确定。这种就属于单个条件的动态SQL语句。
这种需求需要使用到 choose(when,otherwise)标签 实现, 而 choose 标签类似于Java 中的switch语句,对应switch(case, default)。
通过一个案例来使用这些标签
1.5.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义单条件查询的方法。
1 | /** |
1.5.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写 statement,使用 resultMap 而不是使用 resultType
1 | <select id="selectByConditionSingle" resultMap="brandResultMap"> |
1.5.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
执行测试方法结果如下:
1 | // 日志信息 |
1.6 添加数据
我们平时在添加数据时在页面输入想要的数据后添加 提交 按钮,就会将这些数据添加到数据库中。接下来我们就来实现添加数据的操作,暂不需要返回值,后续通过异常判定解决。
-
编写接口方法
1
void add(Brand brand);
参数:除了id之外的所有的数据。id对应的是表中主键值,而主键我们是 自动增长 生成的。
-
编写SQL语句
1
2
3
4<insert id="add">
insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status)
values (#{brandName}, #{companyName}, #{ordered}, #{description}, #{status});
</insert> -
编写测试方法并执行
明确了该功能实现的步骤后,接下来我们进行具体的操作。
1.6.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义添加方法。
1 | /** |
1.6.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写添加数据的 statement
1 | <insert id="add"> |
1.6.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
未提交事务前(未更新到数据库,发生了回滚):
// 日志信息如下:
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.100 [main] o.a.i.t.j.JdbcTransaction- Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.105 [main] c.i.m.B.add -> Preparing: insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.110 [main] c.i.m.B.add -> Parameters: 波导 (String), 波导手机 (String), 1 (Integer), 手机中的战斗机 (String), 1 (Integer)
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.115 [main] c.i.m.B.add -<== Updates: 1
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.120 [main] o.a.i.t.j.JdbcTransaction - Rolling back JDBC Connection
提交事务后,执行结果如下(数据库更新成功):
// 日志信息如下:
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.110 [main] o.a.i.t.j.JdbcTransaction- Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.115 [main] c.i.m.B.add -> Preparing: insert into tb_brand (brand_name, company_name, ordered, description, status) values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.120 [main] c.i.m.B.add -> Parameters: 波导 (String), 波导手机 (String), 1 (Integer), 手机中的战斗机 (String), 1 (Integer)
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.125 [main] c.i.m.B.add -<== Updates: 1
[DEBUG] 21:55:56.130 [main] o.a.i.t.j.JdbcTransaction - Committing JDBC Connection
- MyBatis事务:
- openSession():默认开启事务,进行增删改操作后需要使用sqlSession.commit();手动提交事务
- openSession(true):可以设置为自动提交事务(关闭事务)
1.6.4 添加-主键返回
在数据添加成功后,有时候需要获取插入数据库数据的主键(主键是自增长)。
比如:添加订单和订单项,以下就是一个订单和订单项的例子:
订单数据存储在订单表中,订单项存储在订单项表中。
好的,我给你一个具体的例子来说明订单和订单项的关系以及返回主键的目的。
假设我们有两个表:订单表(orders)和订单项表(order_items)。
订单表包含以下字段:
- order_id (主键)
- customer_id
- order_date
- total_amount
订单项表包含以下字段:
- item_id (主键)
- order_id (外键,与订单表的order_id关联)
- product_id
- quantity
- price
现在我们要添加一笔新的订单,并且需要添加多个订单项。
向订单表中添加订单记录:
假设我们添加了一条订单记录,订单号为"20231127001",顾客ID为"1001",订单日期为"2023-11-27",总金额为"5000元"。数据库会为该订单生成一个唯一的订单主键(order_id)。向订单项表中添加订单项记录:
接下来,我们需要为该订单添加多个订单项。假设订单项1的商品ID为"001",数量为"2",价格为"100元";订单项2的商品ID为"002",数量为"3",价格为"200元"。在添加每个订单项时,我们会使用刚刚生成的订单主键(order_id)作为外键与订单表进行关联。返回主键的作用:
通过返回的订单主键(order_id),我们可以在订单项表中建立订单和订单项之间的关联。每个订单项的记录中都会包含与特定订单关联的订单主键(order_id)。例如,订单项表中的记录可能如下:
2
3
4
--------------------------------------------------------------
1 20231127001 001 2 100元
2 20231127001 002 3 200元通过订单主键(order_id),我们可以轻松地查询特定订单的所有订单项,进行数据的管理和操作。
这就是在订单和订单项中返回主键的具体例子,主键的作用是建立关联、方便查询和管理数据。希望这个例子能够帮助你理解。如果还有其他问题,请随时提问。
明白了什么时候 主键返回 。接下来我们简单模拟一下,在添加完数据后打印id属性值,能打印出来说明已经获取到了。
我们将上面添加品牌数据的案例中映射配置文件里 statement 进行修改,如下
1 | <insert id="add" useGeneratedKeys="true" keyProperty="id"> |
在 insert 标签上添加如下属性:
- useGeneratedKeys:是够获取自动增长的主键值。true表示获取
- keyProperty :指定将获取到的主键值封装到哪儿个属性里
我们用以下代码检验有没有获得主键:
1 | brandMapper.add(brand); |
- 当没有在 insert 标签上添加属性时,执行结果返回
null - 当在 insert 标签上添加属性时,执行结果返回
主键
1.7 修改
在修改页面中,用户在该页面书写需要修改的数据,点击 提交 按钮,就会将数据库中对应的数据进行修改。注意一点,如果哪儿个输入框没有输入内容,我们是将表中数据对应字段值替换为空白还是保留字段之前的值?答案肯定是保留之前的数据。
接下来我们就具体来实现
1.7.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义修改方法,返回结果void和int都可,int表示修改的行数,void会在后面用异常处理。
1 | /** |
上述方法参数 Brand 就是封装了需要修改的数据,而id肯定是有数据的,这也是和添加方法的区别。
1.7.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写修改数据的 statement。
1 | <update id="update"> |
set 标签可以用于动态包含需要更新的列,忽略其它不更新的列,还可解决if语句中逗号的问题。
1.7.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
执行测试方法结果如下:
1 | [DEBUG] main c.i.m.B.update -==> Preparing: update tb_brand SET status = ? where id = ? |
从结果中SQL语句可以看出,只修改了 status 字段值,因为我们给的数据中只给Brand实体对象的 status 属性设置值了。这就是 set 标签的作用。
1.8 删除一行数据
后台管理中一般每行数据后面都有一个 删除 按钮,当用户点击了该按钮,就会将改行数据删除掉。那我们就需要思考,这种删除是根据什么进行删除呢?是通过主键id删除,因为id是表中数据的唯一标识。
接下来就来实现该功能。
1.8.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义根据id删除方法。
1 | /** |
1.8.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写删除一行数据的 statement
1 | <delete id="deleteById"> |
1.8.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
运行过程只要没报错,直接到数据库查询数据是否还存在。
1.9 批量删除
用户还可以选择多条数据,然后点击上面的 删除 按钮,就会删除数据库中对应的多行数据。
1.9.1 编写接口方法
在 BrandMapper 接口中定义删除多行数据的方法。
1 | /** |
参数是一个数组,数组中存储的是多条数据的id
1.9.2 编写SQL语句
在 BrandMapper.xml 映射配置文件中编写删除多条数据的 statement。
编写SQL时需要遍历数组来拼接SQL语句。Mybatis 提供了 foreach 标签供我们使用
foreach 标签
用来迭代任何可迭代的对象(如数组,集合)。
- collection 属性:
- mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合。
- 默认:如果是数组的话,键:“array” = 值: 对应的数组
- 使用@Param注解改变map集合的默认key的名称
- mybatis会将数组参数,封装为一个Map集合。
- item 属性:本次迭代获取到的元素。
- separator 属性:集合项迭代之间的分隔符。
foreach标签不会错误地添加多余的分隔符。也就是最后一次迭代不会加分隔符。 - open 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句之前拼接的语句,只会拼接一次,是左括号
- close 属性:该属性值是在拼接SQL语句拼接后拼接的语句,只会拼接一次,是右括号
1 | <!-- |
假如数组中的id数据是{1,2,3},那么拼接后的sql语句就是:
细节:
如果想要delete标签中collection的值为ids,就需要使用@Param注解,是
void deleteByIds(@Param("ids") int[] ids);
1.9.3 编写测试方法
在 test/java 下的 com.itheima.mapper 包下的 MybatisTest类中 定义测试方法
1 |
|
1.10 Mybatis参数传递
建议:统一都使用@Param注解
Mybatis 接口方法中可以接收各种各样的参数,如下:
- 多个参数
- 单个参数:单个参数又可以是如下类型
- POJO 类型(像我们自定义的User类和Brand类)
- Map 集合类型
- Collection 集合类型
- List 集合类型
- Array 类型
- 其他类型
1.10.1 多个参数
如下面的代码,就是接收两个参数,而接收多个参数需要使用 @Param 注解,那么为什么要加该注解呢?这个问题要弄明白就必须来研究Mybatis 底层对于这些参数是如何处理的。
1 | User select( String username, String password); |
1 | <select id="select" resultType="user"> |
我们在接口方法中定义多个参数,Mybatis 会将这些参数封装成 Map 集合对象,值就是参数值,而键在没有使用 @Param 注解时有以下命名规则:
-
以 arg 开头 :第一个参数就叫 arg0,第二个参数就叫 arg1,以此类推。如:
map.put(“arg0”,参数值1);
map.put(“arg1”,参数值2);
-
以 param 开头 : 第一个参数就叫 param1,第二个参数就叫 param2,依次类推。如:
map.put(“param1”,参数值1);
map.put(“param2”,参数值2);
-
注意:arg0和param1都对应同一个参数值1,同样的,arg1和param2也都对应同一个参数值2,类似以下代码
1
2
3
4map.put("arg0","zhangsan");
map.put("arg1","123");
map.put("param1","zhangsan");
map.put("param2","123")
代码验证:
-
在
UserMapper接口中定义如下方法1
User select(String username,String password);
-
在
UserMapper.xml映射配置文件中定义SQL1
2
3
4
5
6
7<select id="select" resultType="user">
select *
from tb_user
where
username=#{arg0}
and password=#{arg1}
</select>或者
1
2
3
4
5
6
7<select id="select" resultType="user">
select *
from tb_user
where
username=#{param1}
and password=#{param2}
</select> -
运行代码结果如下
1
2
3[DEBUG] main c.i.m.B.select -==> Preparing: select * from tb_user where username = ? and password = ?
[DEBUG] main c.i.m.B.select -==> Parameters: zhangsan(String), 123(String)
[DEBUG] main c.i.m.B.select -==> Total: 1在映射配合文件的SQL语句中使用用
arg开头的和param书写,代码的可读性会变的特别差,此时可以使用@Param注解。
在接口方法参数上使用 @Param 注解,Mybatis 会将 arg 开头的键名替换为对应注解的属性值。
代码验证:
-
在
UserMapper接口中定义如下方法,在username参数前加上@Param注解1
User select( String username, String password);
Mybatis 在封装 Map 集合时,键名就会变成如下:
map.put(“username”,参数值1);
map.put(“arg1”,参数值2);
map.put(“param1”,参数值1);
map.put(“param2”,参数值2);
-
在
UserMapper.xml映射配置文件中定义SQL1
2
3
4
5
6
7<select id="select" resultType="user">
select *
from tb_user
where
username=#{username}
and password=#{param2}
</select> -
运行程序结果没有报错。而如果将
#{}中的username还是写成arg01
2
3
4
5
6
7<select id="select" resultType="user">
select *
from tb_user
where
username=#{arg0}
and password=#{param2}
</select> -
运行程序则可以看到错误
Parameter ‘arg0’ not found.Available parameters are [arg1,param1,username,param2]
// 意思是没有找到arg0这样的参数,参数名称变成了arg1,param1,username,param2
结论:以后接口参数是多个时,在每个参数上都使用 @Param 注解。这样代码的可读性更高。
1.10.2 单个参数
-
POJO 类型
直接使用。要求
属性名和参数占位符名称一致 -
Map 集合类型
直接使用。要求
map集合的键名和参数占位符名称一致 -
Collection 集合类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
map.put(“arg0”,collection集合);
map.put(“collection”,collection集合;
注意:此时两个不同键arg0和collection对应同一个值collections集合
可以使用
@Param注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。 -
List 集合类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
map.put(“arg0”,list集合);
map.put(“collection”,list集合);
map.put(“list”,list集合);
注意:此时三个键对应的都是同一个list集合
可以使用
@Param注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。 -
Array 类型
Mybatis 会将集合封装到 map 集合中,如下:
map.put(“arg0”,数组);
map.put(“array”,数组);
注意:此时两个键对应同一个数组
可以使用
@Param注解替换map集合中默认的 arg 键名。 -
其他类型
比如int类型,
参数占位符名称叫什么都可以。尽量做到见名知意
2,注解实现CRUD(不推荐)
使用注解开发会比配置文件开发更加方便。如下就是使用注解进行开发
1 |
|
注意:
- 注解是用来替换映射配置文件方式配置的,所以使用了注解,就不需要再映射配置文件中书写对应的
statement
Mybatis 针对 CURD 操作都提供了对应的注解,已经做到见名知意。如下:
- 查询 :@Select
- 添加 :@Insert
- 修改 :@Update
- 删除 :@Delete
接下来我们做一个案例来使用 Mybatis 的注解开发
代码实现:
-
将之前案例中
UserMapper.xml中的 根据id查询数据 的statement注释掉 -
在
UserMapper接口的selectById方法上添加注解1
2
User selectById(int id); -
运行测试程序也能正常查询到数据
注解完成简单功能,配置文件完成复杂功能。